Review of Finn 26

Basic specs.

Looking for a new boat? Find a Finn 26 or similar boat for sale
Both the hull and the deck is made of fibreglass. A hull made of fibreglass requires only a minimum of maintenance during the sailing season.

The boat is equipped with 5 berths, a galley, 50 liters (13 US gallons, 10 imperial gallons) fresh water capacity and toilet facility.
The interior is like most other boats made of teak. Teak has the advantage of being naturally very oily and therefore water-repellent, which is suitable on boats.
Note: the boat has also been sold to be home-completed, which means that the quality of each boat may vary.

Finn 26 has more than one rig.
One option is a masthead rig. The advantage of a masthead rig is its simplicity and the fact that a given sail area - compared with a fractional rig - can be carried lower and thus with less heeling moment.
Another option is a fractional rig. The sail area for the mailsail + jib is 22.2 m2 (239.0 ft2). A fractional rig has smaller headsails which make tacking easier, which is an advantage for cruisers and racers, of course. The downside is that having the wind from behind often requires a gennaker or a spinnaker for optimal speed.

Fin keel
The Finn 26 is built with a fin keel. The fin keel is the most common keel and provides splendid manoeuvrability. The downside is that it has less directional stability than a long keel.
The keel is made of iron. Many people prefer lead keel in favour of iron. The main argument is that lead is much heavier than iron and a lead keel can therefore be made smaller which again result in less wet surface, i.e. less drag. In fact iron is quite heavy, just 30% less heavy than lead, so the advantage of a lead keel is often overstated. As the surface of a fin type keel is just a fraction of the total wet surface, the additional surface area created by the cast iron keel in comparison to a lead keel of the same weight would be negligible for cruising yachts.
The boat can enter even shallow marinas as the draft is just about 1.40 - 1.50 meter (4.59 - 4.89 ft) dependent on the load. See immersion rate below.
The fuel tank, which is made of stainless steel, has a capacity of 50 liters (13 US gallons, 10 imperial gallons).
The boat may be equipped with an inboard engine
The transmission is a saildrive.
Sailing characteristics
This section covers widely used rules of thumb to describe the sailing characteristics. Please note that even though the calculations are correct, the interpretation of the results might not be valid for extreme boats.
What is Capsize Screening Formula (CSF)?
The capsize screening value for Finn 26 is 2.11, indicating that this boat would not be accepted to participate in ocean races.
What is Theoretical Maximum Hull Speed?
The theoretical maximal speed of a displacement boat of this length is 6.0 knots. The term "Theoretical Maximum Hull Speed" is widely used even though a boat can sail faster. The term shall be interpreted as above the theoretical speed a great additional power is necessary for a small gain in speed.
The immersion rate is defined as the weight required to sink the boat a certain level.
The immersion rate for Finn 26 is about 116 kg/cm, alternatively 651 lbs/inch.
Meaning: if you load 116 kg cargo on the boat then it will sink 1 cm.
Alternatively, if you load 651 lbs cargo on the boat it will sink 1 inch.
Sailing statistics
This section is statistical comparison with similar boats of the same category. The basis of the following statistical computations is our unique database with more than 26,000 different boat types and 350,000 data points.
What is Motion Comfort Ratio (MCR)?
The Motion Comfort Ratio for Finn 26 is 16.7 - 19.1.
What is L/B (Length Beam Ratio)?
The l/b ratio for Finn 26 is 2.88.
The ballast ratio for Finn 26 is 40%.
What is Displacement Length Ratio?
The DL-ratio for Finn 26 is 263 which categorizes this boat among 'moderate racers'.
What is SA/D (Sail Area Displacement ratio)?
The SA/D for Finn 26 with ISO 8666 reference sail is 15.2, with a 135% genua the SA/D is 18.3.
What is Relative Speed Performance?
The Relative Speed Performance for Finn 26 is 50
Maintenance
When buying anti-fouling bottom paint, it's nice to know how much to buy.
The surface of the wet bottom is about 20m2 (215 ft2).
Based on this, your favourite maritime shop can tell you the quantity you need.
Note: If you use a paint roller you will need more paint than if you use a paintbrush.
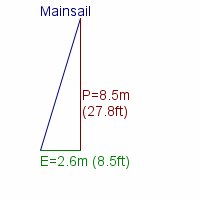
Dimensions of sail for masthead rig.



Are your sails worn out? You might find your next sail here: Sails for Sale
If you need to renew parts of your running rig and is not quite sure of the dimensions, you may find the estimates computed below useful.
| Masthead rig | ||||
| Usage | Length | Diameter | ||
| Mainsail halyard | 22.6 m | (74.0 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Jib/genoa halyard | 22.6 m | (74.0 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Spinnaker halyard | 22.6 m | (74.0 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Jib sheet | 8.1 m | (26.5 feet) | 10 mm | (3/8 inch) |
| Genoa sheet | 8.1 m | (26.5 feet) | 10 mm | (3/8 inch) |
| Mainsheet | 20.2 m | (66.2 feet) | 10 mm | (3/8 inch) |
| Spinnaker sheet | 17.8 m | (58.2 feet) | 10 mm | (3/8 inch) |
| Cunningham | 2.6 m | (8.5 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Kickingstrap | 5.2 m | (17.1 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Clew-outhaul | 5.2 m | (17.1 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Fractional rig | ||||
| Usage | Length | Diameter | ||
| Mainsail halyard | 25.1 m | (82.2 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Jib/genoa halyard | 25.1 m | (82.2 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Spinnaker halyard | 25.1 m | (82.2 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Jib sheet | 8.1 m | (26.5 feet) | 10 mm | (3/8 inch) |
| Genoa sheet | 8.1 m | (26.5 feet) | 10 mm | (3/8 inch) |
| Mainsheet | 20.2 m | (66.2 feet) | 10 mm | (3/8 inch) |
| Spinnaker sheet | 17.8 m | (58.2 feet) | 10 mm | (3/8 inch) |
| Cunningham | 3.2 m | (10.5 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Kickingstrap | 6.4 m | (21.0 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
| Clew-outhaul | 6.4 m | (21.0 feet) | 8 mm | (5/16 inch) |
This section is reserved boat owner's modifications, improvements, etc. Here you might find (or contribute with) inspiration for your boat.
Do you have changes/improvements you would like to share? Upload a photo and describe what you have done.
We are always looking for new photos. If you can contribute with photos for Finn 26 it would be a great help.
If you have any comments to the review, improvement suggestions, or the like, feel free to contact us. Criticism helps us to improve.
